When, Why and How to Scrape with Proxies
by Anas El Mhamdi
Many organizations express interest in using proxies for web scraping without fully understanding when and why they’re necessary. This article clarifies the practical applications of proxies in web scraping, covering when they’re needed, why they matter, and how to implement them effectively.
The Scraping Mind Map
Before diving into proxies, it’s helpful to organize scraping scenarios based on login requirements and data accessibility.
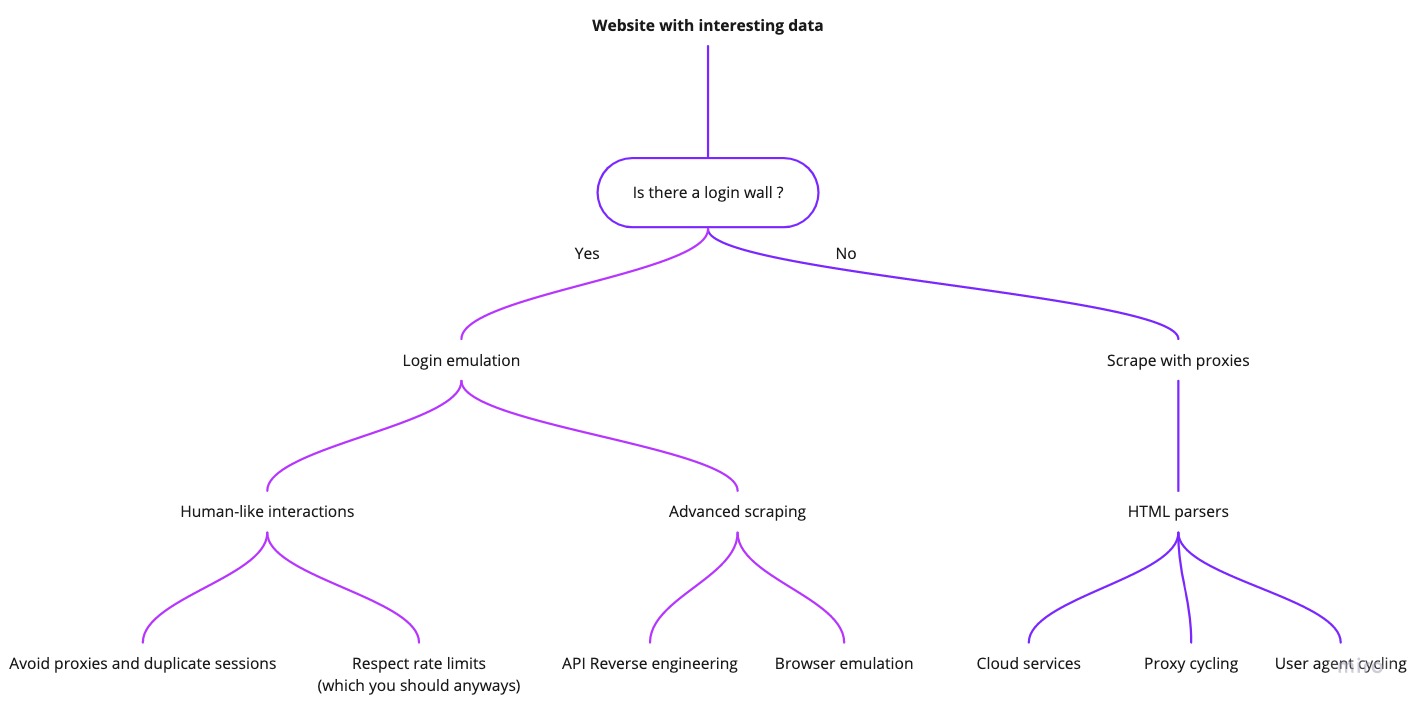
The Login Wall
The first critical question to ask: Can you scrape the same data from public pages instead of requiring login?
Logged-in scraping introduces significant complexity. For example, when reverse engineering the Facebook pages API after login, I discovered that public pages offered nearly identical data without the restrictive limits imposed on authenticated sessions. Always explore public alternatives first.
Scraping Pages Without Login
”Assume you’re being watched”
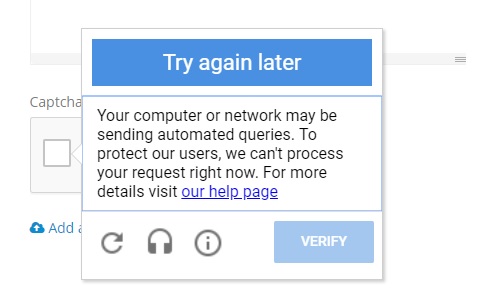
Websites track users by IP address and implement connection limits per user. This fundamental reality shapes how you must approach scraping.
The risks of mass scraping from a single IP:
- IP blacklisting
- Damaged IP reputation affecting multiple sites
- CAPTCHA challenges
- Forced authentication on e-commerce sites
- Severely throttled request speeds
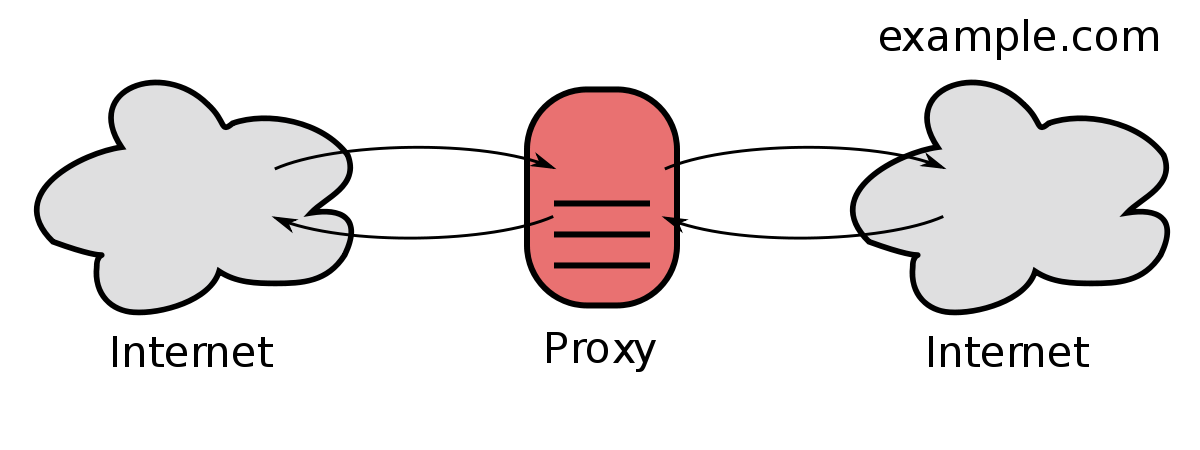
Why Proxies Are Essential
Proxy providers offer multiple IP addresses, making your requests appear to come from multiple different computers connecting simultaneously. This enables scaling scraping operations without bans or slowdowns.

Recommended Proxy Providers:
Free Options:
- pubproxy.com
- Tor network (see my tutorial on scraping with Tor)
Paid Options:
- Zyte - Reliable with easy IP cycling
- Brightdata - Excellent residential IPs, though occasional connection errors may occur
For a detailed comparison, check out this comprehensive proxy services comparison.
Additional Best Practice: User Agent Cycling
Rotating user agents makes requests appear to come from different devices and browsers, further improving script reliability.
Libraries like latest-user-agents help generate legitimate headers. For more information, see the MDN User-Agent documentation and this comprehensive list of user agents for scraping.
Cloud Services
AWS/GCP/Azure

Serverless platforms provision code on random IPs, creating a proxy effect automatically. I recommend using the Serverless framework with AWS Lambda. Check out my guide on creating your own API with AWS Lambda for a quick start.
Specialized Services
- Zyte - Focused on multi-page e-commerce crawling
- Phantombuster & Apify - No-code ready-made tools with customization options
Scraping Login-Required Websites
When scraping requires authentication, two critical questions emerge:
- Which account should you use?
- Can you login from anywhere?
These questions matter significantly for platforms like LinkedIn, Facebook, Twitter, and Amazon.
Account Limits and Human-Like Behavior
Authentication Guidelines:
-
Never access scraping accounts simultaneously from multiple locations - This is an immediate red flag for bot detection systems
-
Avoid random proxy IP changes between logins - Sites detect location discrepancies and will flag your account
-
Use login cookies when viable - For example, LinkedIn’s
_li_at_cookie can maintain sessions without repeated logins -
Match IP location to account location - Inconsistent geography triggers immediate suspension
Best Practices:
Following the principle of “act like a human” is necessary but insufficient alone. You must also respect documented rate limits. Phantombuster has documented limits for popular websites in their support resources.
Technologies for Undetected Scraping
- JavaScript: Puppeteer with the Extra Stealth plugin
- Python: Undetected Chrome Driver
- Tool: Curl Converter helps reverse-engineer browser requests into code
Summary (TL;DR)
-
Always use proxies for public page scraping - Start with lower-quality free options and upgrade as needed
-
Seek alternatives to login-based scraping - If found, return to step one with the public data source
-
Use reverse engineering when login is unavoidable - Employ stealth tools and respect rate limits
-
Respect website automation limits - Never access from multiple IPs or browsers simultaneously; behave like a genuine user
By understanding when and why proxies are necessary, you can build more reliable and sustainable web scraping systems that respect both technical constraints and website policies.